|
|
|
|
|
|
|
such as a bus clock or a periodic interrupt. 3. The 'natural' oscillation frequency of a computer's clock crystal, before frequency division down to the machine's clock rate. 4. A signal emitted at regular intervals by software to demonstrate that it is still alive. Sometimes hardware is designed to reboot the machine if it stops hearing a heartbeat. See also breath-of-life packet. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
heatseeker n. [IBM] A customer who can be relied upon to buy, without fail, the latest version of an existing product (not quite the same as a member of the lunatic fringe). A 1993 example of a heatseeker is someone who, owning a 286 PC and Windows 3.0, goes out and buys Windows 3.1 (which offers no worthwhile benefits unless you have a 386). If all customers were heatseekers, vast amounts of money could be made by just fixing the bugs in each release (n) and selling it to them as release (n+1). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
heavy metal n. [Cambridge] Syn. big iron. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
heavy wizardry n. Code or designs that trade on a particularly intimate knowledge or experience of a particular operating system or language or complex application interface. Distinguished from deep magic, which trades more on arcane theoretical knowledge. Writing device drivers is heavy wizardry; so is interfacing to X (sense 2) without a toolkit. Esp. found in source-code comments of the form "Heavy wizardry begins here". Compare voodoo programming. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
heavyweight adj. High-overhead; baroque; code-intensive; featureful, but costly. Esp. used of communication protocols, language designs, and any sort of implementation in which maximum generality and/or ease of implementation has been pushed at the expense of mundane considerations such as speed, memory utilization, and startup time. EMACS is a heavyweight editor; X is an extremely heavyweight window system. This term isn't pejorative, but one hacker's heavyweight is another's elephantine and a third's monstrosity. Oppose lightweight. Usage: now borders on techspeak, especially in the compound 'heavyweight process'. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
heisenbug /h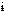 'zen-buhg/ n. [from Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle in quantum physics] A bug that disappears or alters its behavior when one attempts to probe or isolate it. (This usage is not even particularly fanciful; the use of a debugger sometimes alters a program's operating environment significantly enough that buggy code, such as that which relies on the values of uninitialized memory, behaves quite differently.) Antonym of Bohr bug; 'zen-buhg/ n. [from Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle in quantum physics] A bug that disappears or alters its behavior when one attempts to probe or isolate it. (This usage is not even particularly fanciful; the use of a debugger sometimes alters a program's operating environment significantly enough that buggy code, such as that which relies on the values of uninitialized memory, behaves quite differently.) Antonym of Bohr bug; |
|
|
|
|
|