|
|
|
|
|
|
|
to sort all the names into order." See spin; see also grovel. 2. [ETA Systems] To test a wire or printed circuit trace for continuity by applying an AC rather than DC signal. Some wire faults will pass DC tests but fail a buzz test. 3. To process an array or list in sequence, doing the same thing to each element. "This loop buzzes through the tz array looking for a terminator type." |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BWQ /B-W-Q/ n. [IBM: abbreviation, 'Buzz Word Quotient'] The percentage of buzzwords in a speech or documents. Usually roughly proportional to bogosity. See TLA. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
by hand adv. 1. Said of an operation (especially a repetitive, trivial, and/or tedious one) that ought to be performed automatically by the computer, but which a hacker instead has to step tediously through. "My mailer doesn't have a command to include the text of the message I'm replying to, so I have to do it by hand." This does not necessarily mean the speaker has to retype a copy of the message; it might refer to, say, dropping into a subshell from the mailer, making a copy of one's mailbox file, reading that into an editor, locating the top and bottom of the message in question, deleting the rest of the file, inserting '>' characters on each line, writing the file, leaving the editor, returning to the mailer, reading the file in, and later remembering to delete the file. Compare eyeball search. 2. By extension, writing code which does something in an explicit or low-level way for which a presupplied library routine ought to have been available. "This cretinous Btree library doesn't supply a decent iterator, so I'm having to walk the trees by hand." |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
byte /b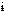 t/ n. [techspeak] A unit of memory or data equal to the amount used to represent one character; on modern architectures this is usually 8 bits, but may be 9 on 36-bit machines. Some older architectures used 'byte' for quantities of 6 or 7 bits, and the PDP-10 supported 'bytes' that were actually bitfields of 1 to 36 bits! These usages are now obsolete, and even 9-bit bytes have become rare in the general trend toward power-of-2 word sizes. t/ n. [techspeak] A unit of memory or data equal to the amount used to represent one character; on modern architectures this is usually 8 bits, but may be 9 on 36-bit machines. Some older architectures used 'byte' for quantities of 6 or 7 bits, and the PDP-10 supported 'bytes' that were actually bitfields of 1 to 36 bits! These usages are now obsolete, and even 9-bit bytes have become rare in the general trend toward power-of-2 word sizes. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Historical note: The term was coined by Werner Buchholz in 1956 during the early design phase for the IBM Stretch computer; originally it was described as 1 to 6 bits (typical I/O equipment of the period used 6-bit chunks of information). The move to an 8-bit byte happened in late 1956, and this size was later adopted and promulgated as a standard by the System/360. The word was coined by mutating the word 'bite' so it would not be accidentally misspelled as bit. See also nybble. |
|
|
|
|
|